A Network discovery tool can help find everything that is connected to a network, create topology maps, and generate reports. These type of software scans the entire network, identify its components, and creates an inventory. With this information, the software can create visualizations of the physical and virtual network connectivity. The graph rearranges itself in a smooth animation to reflect the new view of the network. Run a new scan and every new host and network path will be added to the topology automatically. The topology view is most useful when combined with Nmap's -traceroute option, because that's the option that discovers the network path to a host. Nmap stands for “network mapper”, and this is pretty explanatory. In fact, nmap is a tool that allows you to create a detailed map of a network. As we will see later in this nmap tutorial, you can use this tool to have a clear picture of the network. To start, we can reconstruct the topology, identifying all the devices in the network.
Modern businesses can’t function without aninternal network, where data and files are kept and shared by the employees.Businesses, whether big or small, need to have experienced IT staff to protectthe company’s network from data theft and interference. If you think yourbusiness is too small for cybercriminals to notice, it’s time to review yoursecurity measures. As per the statistics published by Verizon 2019 Data BreachInvestigations Report (DBIR), approximately 43% of all cyber-attacks targetedsmall businesses.
Hackers utilize vulnerability scanners to searchfor loopholes in the network. A vulnerable network is easy to hack and can posea huge threat to the system and sensitive information. Thus, it’s imperative tocheck your network’s security rigorously and regularly.
Regular scanning of your network allows you tokeep track of the devices on your network, view how they’re performing, spotthe flaws, and understand the flow of traffic between connected devices andapplications. Thus, network scanning is a process helping admins gatherinformation from all devices or endpoints on a network. During a network scan,all the active devices on the network send signals, and once the response isreceived, the scanner evaluates the results and checks to see if there areinconsistencies.
Network scanning allows companies to:
- Keep a tab on the available UDP and TCP networkservices
- Access the operating systems in use bymonitoring the IP responses
- Identify the filtering systems between nodes
Network scanning involves network port scanningand vulnerability scanning.
In port scanning, the scanner sends data packetsto a specified service port number over the network. This helps to identify theavailable network services on a particular system for troubleshooting.
Vulnerability scanning allows the scanner todetect known vulnerabilities of computing systems available on a network. Thisprocess helps the scanner to identify specific weak spots in applicationsoftware or the operating system.
Both network port and vulnerability scanninggather relevant information from the network. This information, when used byunauthorized personnel, poses a serious threat to the company.
Network scanning is also closely related to packetsniffing or passive scanning.
Passive scanning captures and tracks the flow ofdata packets over the network. Packet-level traffic on your network can betracked by implementing sensors on the devices and using tools to translatepacket data into relevant information easily. With this approach, the scannerevaluates the traffic flow as soon as the devices start sending messages to thenetwork, without having to ping the devices separately.
Although passive scanning is an important partof your toolkit, it has some limitations. The passive scanner cannot detectthose devices or applications not communicating.
How Does a Network Scan Work?
Network scanning helps to detect all the activehosts on a network and maps them to their IP addresses. Network scanners send apacket or ping to every possible IP address and wait for a response todetermine the status of the applications or devices (hosts). The respondinghosts are considered active, while others are considered dead or inactive.These responses are then scanned to detect inconsistencies.
Using an Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) scan,admins can manually ping the subnet. But for a wider reach across all subnets,it’s better to use tools capable of automatically running scans and discoveringdevices. Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) scans allow you to mapnetwork topology.
To keep the networking systems up and running, companies need to rely on robust Network scanning tools. A Network scanning tool is essential for companies who have a large network with multiple subnets. The companies must always invest in those scanners providing flexibility with the changing requirements. The chosen network scanner should be able to scale up easily with time as per the network security requirements without having to incur any substantial additional costs. Some of the top scanning tools available in the market include Swascan, Spyse, Acunetix, SolarWinds® IP Address Manager, SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor, and Nikto. We have discussed a couple of these tools in detail below:
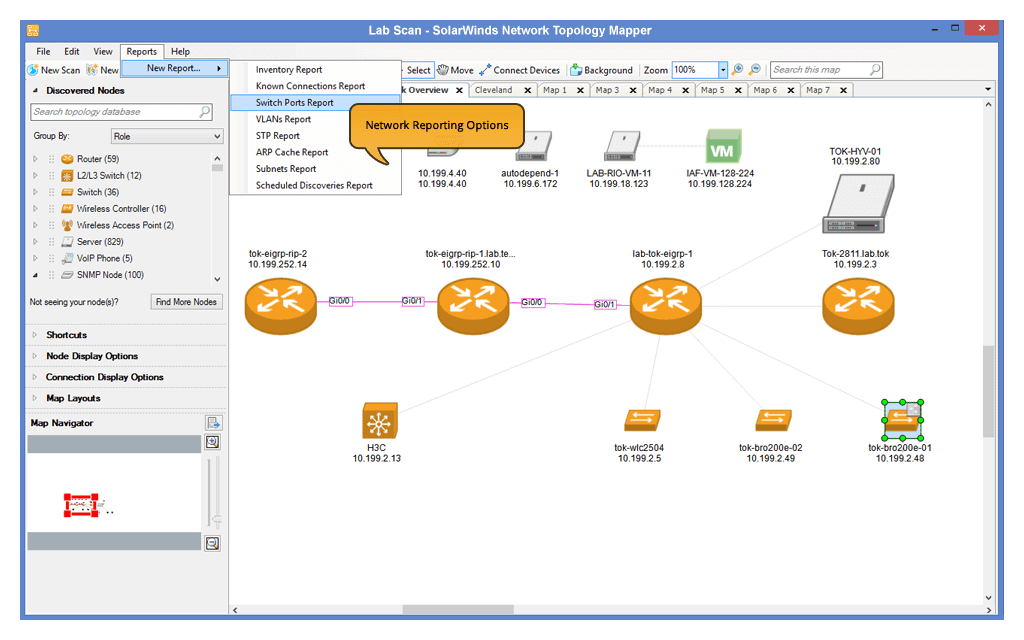
SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor (NPM)
SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor can scan your network automatically. This tool uses passive scanning to show critical information regarding your network. This tool also functions as a network discovery and performance management tool. It allows companies to create network topologies and helps to keep a check on the devices and applications on your network. With functions like Heat Maps and Comparative Graphs for intelligent visualizations, it’s possible to understand the network from a node-by-node perspective. The network information retrieved from this tool can further be used to detect possible anomalies.
Network Topology
SolarWinds IP Address Manager (IPAM)
SolarWinds IP Address Manager is a network scanning tool which uses IP addresses to manage devices. Companies can do away with bulky IP tracking spreadsheets and use this tool to scan and discover IPv4 and IPv6 addresses across subnets actively.
- Using IPAM, companies can monitor the usage of IP addresses, spot mismatched DNS entries, and quickly rectify issues related to subnet capacity and IP address conflicts.
- IPAM allows admins to manage DHCP and DNS servers from a centralized console. Admins can also monitor resource records and manage the DNS zones.
- IPAM allows users to create, modify, and delete IP records in IPv4 and IPv6 environments. Using API, users can also create new subnets in IPAM and create, update, or remove DNS entries.
- The users can automatically reserve IP addresses by utilizing the built-in IP Request Form.
- IPAM provides a detailed history of all the past and current IP addresses along with the status of subnets to effectively allocate them for the future.
- The advanced alerting tools in IPAM help the network admins to catch IP-related problems instantly. SolarWinds IP tracker software allows admins to easily monitor different MAC address changes and IP conflicts.
Ring Topology Lan
Conclusion
In today’s world, every company, be it big orsmall, strives hard to safeguard its devices and systems from unauthorizedaccess. The companies must have a prevention plan in hand to avoid futureattacks on the network. They need to invest in robust network scanning tools tosecure their system against potential cyberattacks without compromising withthe performance. Before choosing a tool, they need to take time to understand whichtype of scanning tool is a perfect fit for their network. The admins need toimplement the right sensors and tools to protect the systems from being hackedalong with a robust scanner to translate packet data into easily readableinformation.
Modern businesses can’t function without aninternal network, where data and files are kept and shared by the employees.Businesses, whether big or small, need to have experienced IT staff to protectthe company’s network from data theft and interference. If you think yourbusiness is too small for cybercriminals to notice, it’s time to review yoursecurity measures. As per the statistics published by Verizon 2019 Data BreachInvestigations Report (DBIR), approximately 43% of all cyber-attacks targetedsmall businesses.
Hackers utilize vulnerability scanners to searchfor loopholes in the network. A vulnerable network is easy to hack and can posea huge threat to the system and sensitive information. Thus, it’s imperative tocheck your network’s security rigorously and regularly.
Regular scanning of your network allows you tokeep track of the devices on your network, view how they’re performing, spotthe flaws, and understand the flow of traffic between connected devices andapplications. Thus, network scanning is a process helping admins gatherinformation from all devices or endpoints on a network. During a network scan,all the active devices on the network send signals, and once the response isreceived, the scanner evaluates the results and checks to see if there areinconsistencies.
Network scanning allows companies to:
- Keep a tab on the available UDP and TCP networkservices
- Access the operating systems in use bymonitoring the IP responses
- Identify the filtering systems between nodes
Network scanning involves network port scanningand vulnerability scanning.
In port scanning, the scanner sends data packetsto a specified service port number over the network. This helps to identify theavailable network services on a particular system for troubleshooting.
Vulnerability scanning allows the scanner todetect known vulnerabilities of computing systems available on a network. Thisprocess helps the scanner to identify specific weak spots in applicationsoftware or the operating system.
Both network port and vulnerability scanninggather relevant information from the network. This information, when used byunauthorized personnel, poses a serious threat to the company.
Network scanning is also closely related to packetsniffing or passive scanning.
Passive scanning captures and tracks the flow ofdata packets over the network. Packet-level traffic on your network can betracked by implementing sensors on the devices and using tools to translatepacket data into relevant information easily. With this approach, the scannerevaluates the traffic flow as soon as the devices start sending messages to thenetwork, without having to ping the devices separately.
Although passive scanning is an important partof your toolkit, it has some limitations. The passive scanner cannot detectthose devices or applications not communicating.
How Does a Network Scan Work?
Network scanning helps to detect all the activehosts on a network and maps them to their IP addresses. Network scanners send apacket or ping to every possible IP address and wait for a response todetermine the status of the applications or devices (hosts). The respondinghosts are considered active, while others are considered dead or inactive.These responses are then scanned to detect inconsistencies.
Using an Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) scan,admins can manually ping the subnet. But for a wider reach across all subnets,it’s better to use tools capable of automatically running scans and discoveringdevices. Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) scans allow you to mapnetwork topology.
To keep the networking systems up and running, companies need to rely on robust Network scanning tools. A Network scanning tool is essential for companies who have a large network with multiple subnets. The companies must always invest in those scanners providing flexibility with the changing requirements. The chosen network scanner should be able to scale up easily with time as per the network security requirements without having to incur any substantial additional costs. Some of the top scanning tools available in the market include Swascan, Spyse, Acunetix, SolarWinds® IP Address Manager, SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor, and Nikto. We have discussed a couple of these tools in detail below:
SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor (NPM)
Lan Topology Scanner Definition
SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor can scan your network automatically. This tool uses passive scanning to show critical information regarding your network. This tool also functions as a network discovery and performance management tool. It allows companies to create network topologies and helps to keep a check on the devices and applications on your network. With functions like Heat Maps and Comparative Graphs for intelligent visualizations, it’s possible to understand the network from a node-by-node perspective. The network information retrieved from this tool can further be used to detect possible anomalies.
SolarWinds IP Address Manager (IPAM)
SolarWinds IP Address Manager is a network scanning tool which uses IP addresses to manage devices. Companies can do away with bulky IP tracking spreadsheets and use this tool to scan and discover IPv4 and IPv6 addresses across subnets actively.
- Using IPAM, companies can monitor the usage of IP addresses, spot mismatched DNS entries, and quickly rectify issues related to subnet capacity and IP address conflicts.
- IPAM allows admins to manage DHCP and DNS servers from a centralized console. Admins can also monitor resource records and manage the DNS zones.
- IPAM allows users to create, modify, and delete IP records in IPv4 and IPv6 environments. Using API, users can also create new subnets in IPAM and create, update, or remove DNS entries.
- The users can automatically reserve IP addresses by utilizing the built-in IP Request Form.
- IPAM provides a detailed history of all the past and current IP addresses along with the status of subnets to effectively allocate them for the future.
- The advanced alerting tools in IPAM help the network admins to catch IP-related problems instantly. SolarWinds IP tracker software allows admins to easily monitor different MAC address changes and IP conflicts.
Conclusion
Star Topology Lan
In today’s world, every company, be it big orsmall, strives hard to safeguard its devices and systems from unauthorizedaccess. The companies must have a prevention plan in hand to avoid futureattacks on the network. They need to invest in robust network scanning tools tosecure their system against potential cyberattacks without compromising withthe performance. Before choosing a tool, they need to take time to understand whichtype of scanning tool is a perfect fit for their network. The admins need toimplement the right sensors and tools to protect the systems from being hackedalong with a robust scanner to translate packet data into easily readableinformation.